profile 、bashrc 等文件的区别和联系
一般配置环境变量时会用到这几个文件,那么这几个文件究竟有什么区别和联系呢?
下面从两个方面简单说下:
区别
几个文件的作用域不一样,etc 下面的是对所有用户的, home目录下的只针对 shell 登录用户
/etc/profile
此文件为系统的每个用户设置环境信息,当用户第一次登录时,该文件被执行.并从/etc/profile.d目录的配置文件中搜集shell的设置.
所以如果你有对/etc/profile有修改的话必须得重启你的修改才会生效,此修改对每个用户都生效。
/etc/bash.bashrc
为每一个运行bash shell的用户执行此文件. 当bash shell被打开时,该文件被读取.每次用户打开一个终端时,执行此文件
如果你想对所有的使用bash的用户修改某个配置并在以后打开的bash都生效的话可以修改这个文件,修改这个文件也需要重启。
~/.bash_profile 、~/.bash_login 、~/.profile
三个文件中往往系统中往往只存在一个,在不同的发行版中不同,如CentOS和RedHat中是
~/.bash_profile,而Debian和Ubuntu等系列中往往是~/.profile但是 三个文件还是有个优先级,
~/.bash_profile>~/.bash_login>~/.profile所以自己不要随便增加文件,以避免出现其他问题
~/.bash_profile
每个用户都可使用该文件输入专用于自己使用的shell信息,当用户登录时,该文件仅仅执行一次!默认情况下,他设置一些环境变量,执行用户的.bashrc文件
此文件类似于/etc/profile,也是需要需要重启才会生效,/etc/profile对所有用户生效,~/.bash_profile只对当前用户生效
~/.bash_login
~/.profile
在Debian中使用.profile文件代 替.bash_profile文件
.profile(由Bourne Shell和Korn Shell使用)和.login(由C Shell使用)两个文件是.bash_profile的同义词,目的是为了兼容其它Shell。在Debian中使用.profile文件代 替.bash_profile文件。
~/.bashrc
该文件包含专用于你的bash shell的bash信息,当登录时以及每次打开新的shell时,该文件被读取.
执行顺序
我们可以做个实验:
以下实验都是在 20.04.2 LTS 中进行的,所有文件都是默认配置
在 每个文件里追加 添加
echo "{filename} ... ..."
文件开始添加:
echo -e "\033[32m---------- {filename} ... ... ---------- \033[0m"
文件结尾添加:
echo -e "\033[32m---------- {filename} . end ---------- \033[0m"
开机执行的顺序
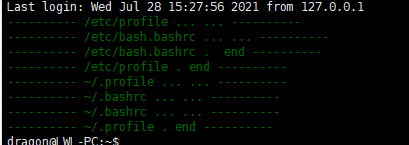
开机登录该用户读取顺序:
/etc/profile->/etc/bash.bashrc->~/.profile->~/.bashrc
source 文件
$ source /etc/profile
---------- /etc/profile ... ... ----------
---------- /etc/bash.bashrc ... ... ----------
---------- /etc/bash.bashrc . end ----------
---------- /etc/profile . end ----------
$ source .profile
---------- ~/.profile ... ... ----------
---------- ~/.bashrc ... ... ----------
---------- ~/.bashrc ... ... ----------
---------- ~/.profile . end ----------
$ source /etc/bash.bashrc
---------- /etc/bash.bashrc ... ... ----------
---------- /etc/bash.bashrc . end ----------
$ source .bashrc
---------- ~/.bashrc ... ... ----------
---------- ~/.bashrc ... ... ----------
由于
/etc/profile文件内执行了source /etc/bash.bashrc所以在执行source /etc/profile时 也会读取/etc/bash.bashrc文件同理
~/.profile文件内执行了source ~/.bashrc所以在执行source ~/.profile时 也会读取~/.bashrc文件
su 切换到该用户
不带参数
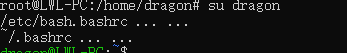
/etc/bash.bashrc->~/.bashrc
带-l参数
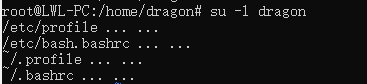
/etc/profile->/etc/bash.bashrc->~/.profile->~/.bashrc
执行shell 脚本
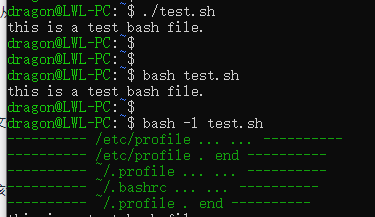
./test.sh 和 bash test.sh 不会读取上述文件
bash -l test.sh 执行顺序 :
/etc/profile->~/.profile->~/.bashrc